马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能,让你轻松玩转社区。
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
x
来吧,开始记笔记!!!
类的默认成员函数
默认成员函数,简单来说,就是我们不写,编译器会主动生成的一些函数,没有显示的实现
默认成员函数就是⽤⼾没有显式实现,编译器会⾃动⽣成的成员函数称为默认成员函数。⼀个类,我 们不写的环境下编译器会默认⽣成以下6个默认成员函数,需要注意的是这6个中最重要的是前4个,最 后两个取地点重载不重要, 其次就是C++11以后还会增加两个默认成员函数, 移动构造和移动赋值,这两个背面在说。 默认成员函数很重要,也⽐较复杂,我们要从两个⽅⾯ 去学习: • 第⼀:我们不写时,编译器默认⽣成的函数⾏为是什么,是否满⾜我们的需求。 • 第⼆:编译器默认⽣成的函数不满⾜我们的需求,我们需要⾃⼰实现,那么如何⾃⼰实现? 只有知道第一点,我们才知道我们到底需不需要写(默认生成的函数是否符合我们的需求) 总体框架: 1.构造函数(最复杂)
构造函数是特殊的成员函数,需要注意的是,构造函数固然名称叫构造,但是构造函数的主要任务并不是开空间创建对象(我们常使⽤的局部对象是栈帧创建时,空间就开好了),⽽是对象实例化时初始化对象。构造函数的本质是要替代我们以前Stack和Date类中写的Init函数(初始化)的功能,构造函数⾃动调⽤的特点就完美的替代的了Init。 构造函数的特点: 1. 函数名与类名相同; 2. ⽆返回值; (返回值啥都不需要给,也不需要写void,不要纠结,C++规定云云) 3. 对象实例化时系统会⾃动调⽤对应的构造函数; 4. 构造函数可以重载;(也就是可以函数重载) 代码演示: - #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Date
- {
- public:
- // 1.⽆参构造函数
- Date()
- {
- _year = 1;
- _month = 1;
- _day = 1;
- }
- // 2.带参构造函数
- Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- _year = year;
- _month = month;
- _day = day;
- }
-
- void Print()
- {
- cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
- }
- private:
- int _year;
- int _month;
- int _day;
- };
- int main()
- {
- //调用第一个:默认构造函数
- Date d1;
- d1.Print();
- //调用第二个:带参的构造函数(函数重载),可以按F11去看看
- Date d2(2024, 7, 15);
- d2.Print();
- //注意:无参不能加括号,对象没有被定义出来,因为和函数声明区分不开
- //Date d3();
- //d3.Print();
- //函数声明样例:
- //Date func();
- //func.Print();
- return 0;
- }
- class Date
- {
- public:
- // 全缺省构造函数(全缺省和无参,是函数重载,但存在调用歧义)(可以兼备前两个)
- Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
- {
- _year = year;
- _month = month;
- _day = day;
- }
- void Print()
- {
- cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
- }
- private:
- int _year;
- int _month;
- int _day;
- };
- int main()
- {
- Date d1;
- d1.Print();
- Date d2(2024, 7, 15);
- d2.Print();
- Date d3(2024);
- d3.Print();
- return 0;
- }
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- typedef int STDataType;
- class Stack
- {
- public:
- //当没有默认构造时:Stack(int n)//会报错:这自己生成不了了·······
- Stack(int n = 4)//因为缺省,知道多少给多少,不知道的就默认给4,有效避免了扩容带来的空间浪费
- {
- _a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);
- if (nullptr == _a)
- {
- perror("malloc申请空间失败");
- return;
- }
- _capacity = n;
- _top = 0;
- }
- // ...
- private://栈不自己写,下面给随机值,这不就扯蛋吗
- STDataType* _a;
- size_t _capacity;
- size_t _top;
- int size;//自动生成的构造对内置类型的初始化是不确定的//加这句就是一个坑,但也有方法可以解决
- };
- // 两个Stack实现队列
- class MyQueue
- {
- public:
- //编译器默认⽣成MyQueue的构造函数调⽤了Stack的构造,完成了两个成员的初始化
- private:
- Stack pushst;//重Stack中找,我们写的全缺省Stack就是他要调用的默认构造函数
- Stack popst;
- };
- int main()
- {
- MyQueue mq;
- return 0;
- }
析构函数与构造函数功能相反,析构函数不是完成对对象本⾝的销毁,⽐如局部对象是存在栈帧的,函数结束栈帧销毁,他就释放了,不需要我们管,C++规定对象在销毁时会⾃动调⽤析构函数,完成对象中资源的清理释放⼯作。析构函数的功能类⽐我们之前Stack实现的Destroy功能,⽽像Date没有Destroy,其实就是没有资源需要释放,所以严酷说Date是不需要析构函数的。 析构函数的特点:(针对有资源申请的类)
1. 析构函数名是在类名前加上字符 ~;(联想按位取反“~”) 2. ⽆参数⽆返回值; (这⾥跟构造雷同,也不需要加void) 3. ⼀个类只能有⼀个析构函数,若未显式界说,系统会⾃动⽣成默认的析构函数; 4. 对象⽣命周期结束时,系统会⾃动调⽤析构函数; 5. 跟构造函数雷同,我们不写编译器⾃动⽣成的析构函数对内置类型成员不做处理,⾃定类型成员会调⽤他的析构函数; 6. 还需要注意的是我们显⽰写析构函数,对于⾃界说类型成员也会调⽤他的析构,也就是说⾃界说类型成员⽆论什么环境都会⾃动调⽤析构函数; 7. 如果类中没有申请资源时,析构函数可以不写,直接使⽤编译器⽣成的默认析构函数,如Date;如果默认⽣成的析构就可以⽤,也就不需要显⽰写析构,如MyQueue;但是有资源申请时,⼀定要⾃⼰写析构,否则会造成资源走漏,如Stack; 8. ⼀个局部域的多个对象,C++规定后界说的先析构; - #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- typedef int STDataType;
- class Stack
- {
- public:
- Stack(int n = 4)
- {
- _a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);
- if (nullptr == _a)
- {
- perror("malloc申请空间失败");
- return;
- }
- _capacity = n;
- _top = 0;
- }
- ~Stack()
- {
- cout << "~Stack()" << endl;
- free(_a);
- _a = nullptr;
- _top = _capacity = 0;
- }//不写就内存泄漏了
- private:
- STDataType* _a;
- size_t _capacity;
- size_t _top;
- };
- // 两个Stack实现队列
- class MyQueue
- {
- public:
- //编译器默认⽣成MyQueue的析构函数调⽤了Stack的析构,释放的Stack内部的资源
- //显⽰写析构,也会⾃动调⽤Stack的析构
- //还需要注意的是我们显⽰写析构函数,对于⾃定义类型成员也会调⽤他的析构,也就是说⾃定义类型成员⽆论什么情况都会⾃动调⽤析构函数;
- /*~MyQueue()
- {}*/
- private:
- Stack pushst;
- Stack popst;
- };
- int main()//在类中想要看成员变量,在调试的时候直接写一个this,就可以看到成员了
- {
- Stack st;
- MyQueue mq;//如果有多个对象,后定义的先析构(规定)
- return 0;
- }
如果⼀个构造函数的第⼀个参数是⾃⾝类类型的引⽤(只要求是第一个),且任何额外的参数都有默认值(缺省值),则此构造函数也叫做拷⻉构造函数,也就是说拷⻉构造是⼀个特殊的构造函数 1. 拷⻉构造函数是构造函数的⼀个重载; - #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Date
- {
- public:
- Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
- {
- _year = year;
- _month = month;
- _day = day;
- }
- //拷贝函数
- //第一的参数:类类型的引用
- //Date(const Date& d , int x = 0)//其他的一定要是默认值/缺省值,但一般不用
- //Date(const Date)//使用传值方式编译器会报错
- Date(const Date& d)
- {
- _year = d._year;
- _month = d._month;
- _day = d._day;
- }
- void Print()
- {
- cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
- }
- private:
- int _year;
- int _month;
- int _day;
- };
- int main()
- {
- //用常规值初始化
- Date d1(2024, 7, 16);
- d1.Print();
- //用d1拷贝d2
- //调用的就是拷贝构造
- Date d2(d1);
- d2.Print();
- return 0;
- }
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Date
- {
- public:
- Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
- {
- _year = year;
- _month = month;
- _day = day;
- }
- Date(const Date& d)
- {
- _year = d._year;
- _month = d._month;
- _day = d._day;
- }
- void Print()
- {
- cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
- }
- private:
- int _year;
- int _month;
- int _day;
- };
- //为什么必须是引用?
- void Func1(Date d)
- {
- cout << &d << endl;
- d.Print();
- }
- int main()
- {
- Date d1(2024, 7, 16);
- d1.Print();
- //C++规定传值传参要调用拷贝构造函数,C语言传直接按字节拷贝过去了
- Func1(d1);//调试发现,按F11并没有跳到Func1函数中,而是跳到了拷贝构造函数中,再跳到Func,本质是调用了两个函数
- }
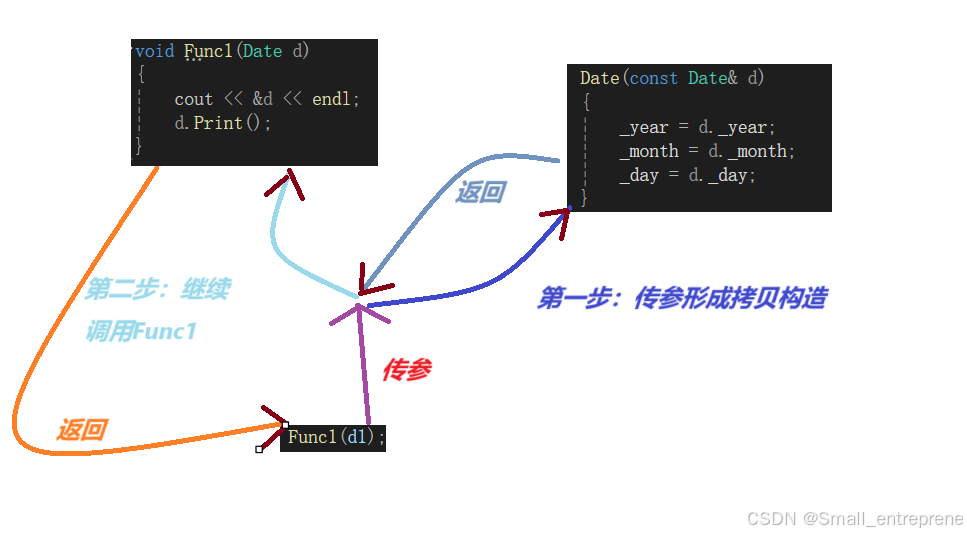
图解:
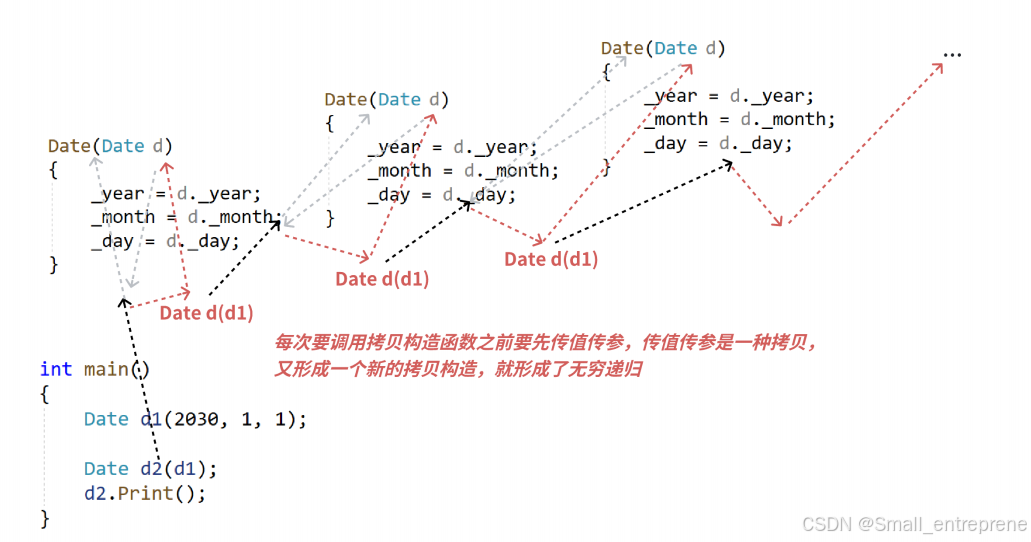
用引用的话,d是d1的别名,所以传参的时候不会形成新的拷贝构造
4. 若未显式界说拷⻉构造,编译器会⽣成⾃动⽣成拷⻉构造函数。⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造对内置类型(构造函数:(初始化不确定)和析构函数:(不处理)对内置类型是不做处理的)成员变量会完成值拷⻉/浅拷⻉(⼀个字节⼀个字节的拷⻉),对⾃界说类型成员变量会调⽤他的拷⻉构造;(内置类型拷贝构造也管) - #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Date
- {
- public:
- Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
- {
- _year = year;
- _month = month;
- _day = day;
- }
- /*Date(const Date& d)
- {
- _year = d._year;
- _month = d._month;
- _day = d._day;
- }*/
- void Print()
- {
- cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
- }
- private:
- int _year;
- int _month;
- int _day;
- };
- int main()
- {
- //⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造对内置类型成员变量会完成值拷⻉/浅拷⻉
- //照样可以拷贝
- Date d1(2024, 7, 17);
- d1.Print();
- Date d2(d1);
- d2.Print();
- //2024 / 7 / 17
- //2024 / 7 / 17
- return 0;
- }
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- typedef int STDataType;
- class Stack
- {
- public:
- Stack(int n = 4)
- {
- _a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);
- if (nullptr == _a)
- {
- perror("malloc申请空间失败");
- return;
- }
- _capacity = n;
- _top = 0;
- }
- void Push(STDataType x)
- {
- if (_top == _capacity)
- {
- int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *
- sizeof(STDataType));
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc fail");
- return;
- }
- _a = tmp;
- _capacity = newcapacity;
- }
- _a[_top++] = x;
- }
- ~Stack()
- {
- cout << "~Stack()" << endl;
- free(_a);
- _a = nullptr;
- _top = _capacity = 0;
- }
- private:
- STDataType* _a;
- size_t _capacity;
- size_t _top;
- };
- int main()
- {
- Stack st1;
- st1.Push(1);
- st1.Push(2);
- // Stack不显⽰实现拷⻉构造,⽤⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造完成浅拷⻉
- // 会导致st1和st2⾥⾯的_a指针指向同⼀块资源,析构时会析构两次,程序崩溃
- Stack st2(st1);
- //Stack st3 = st1;//拷贝构造也可以这么写
- return 0;
- }
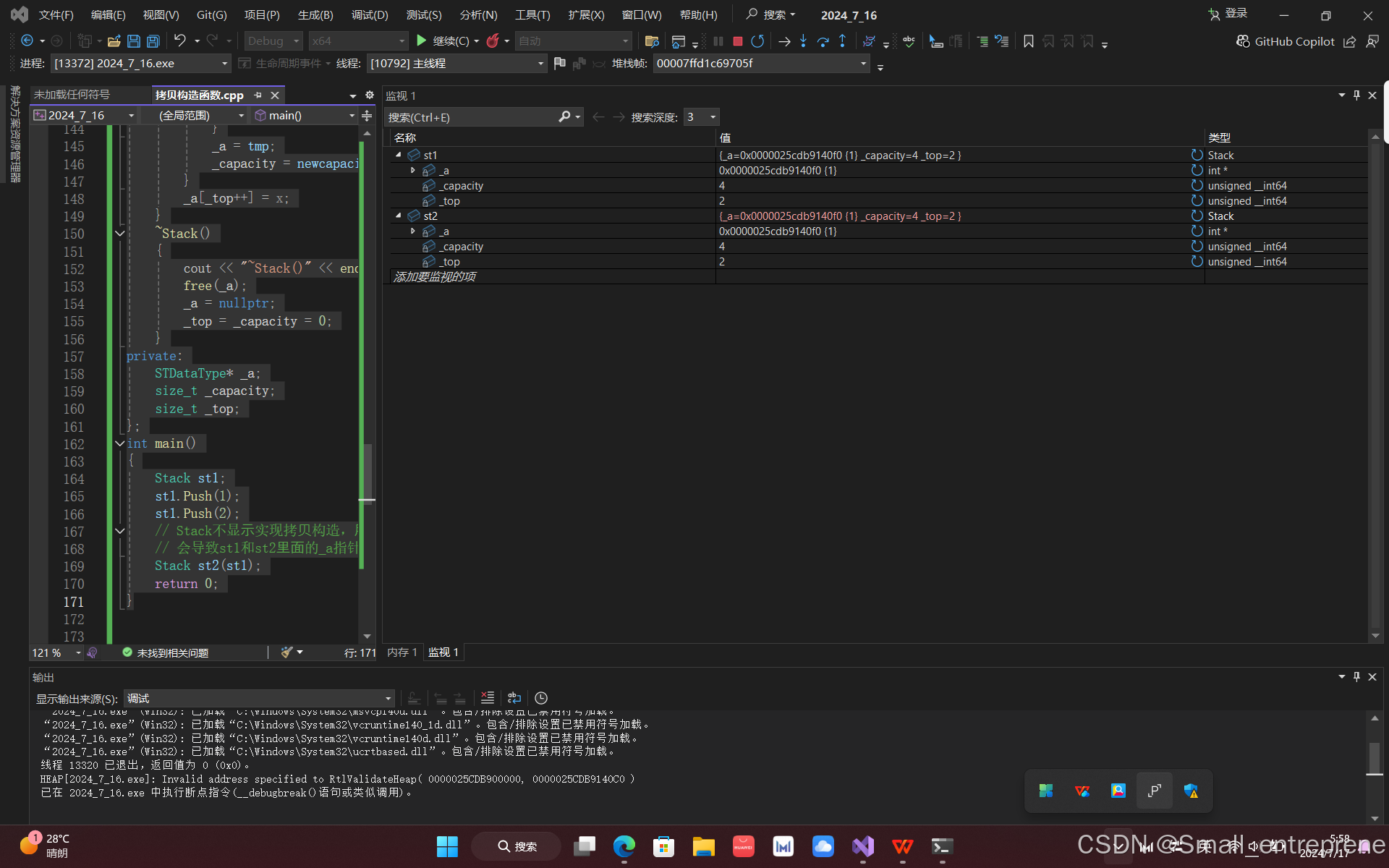
发现题目:
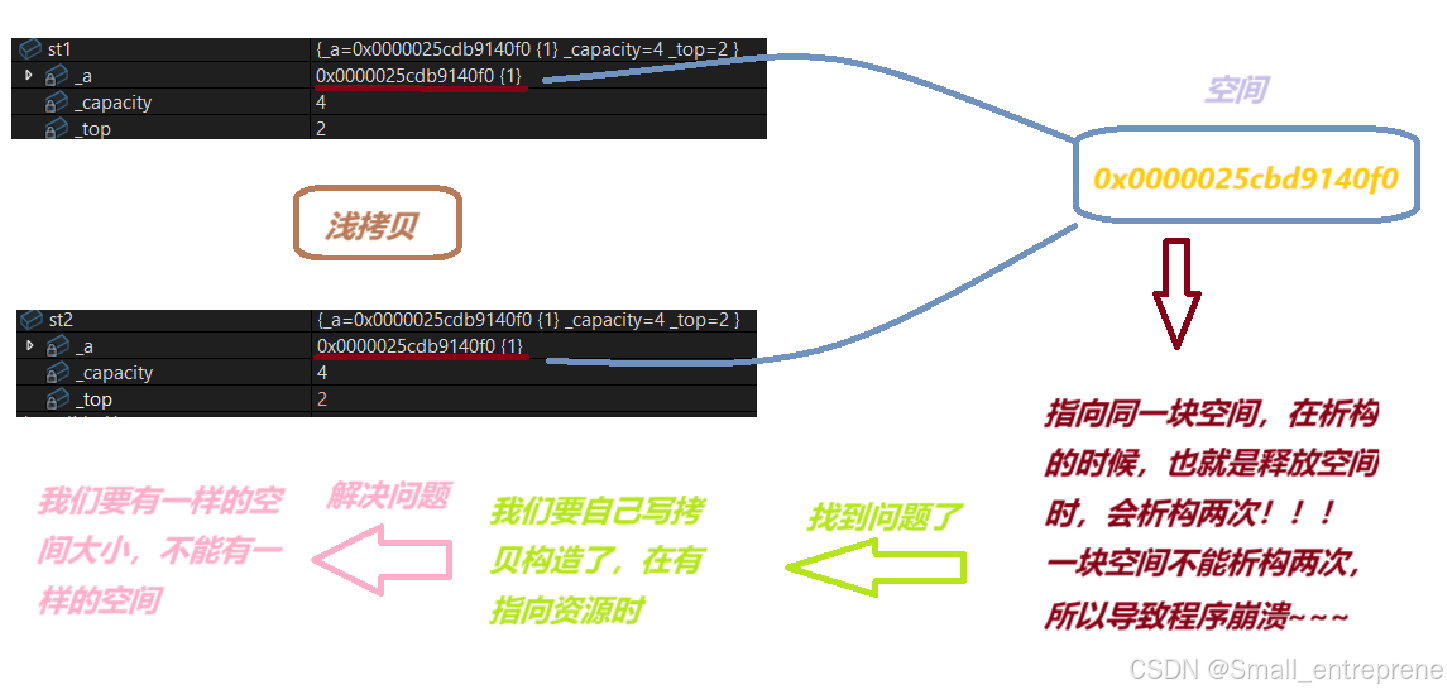
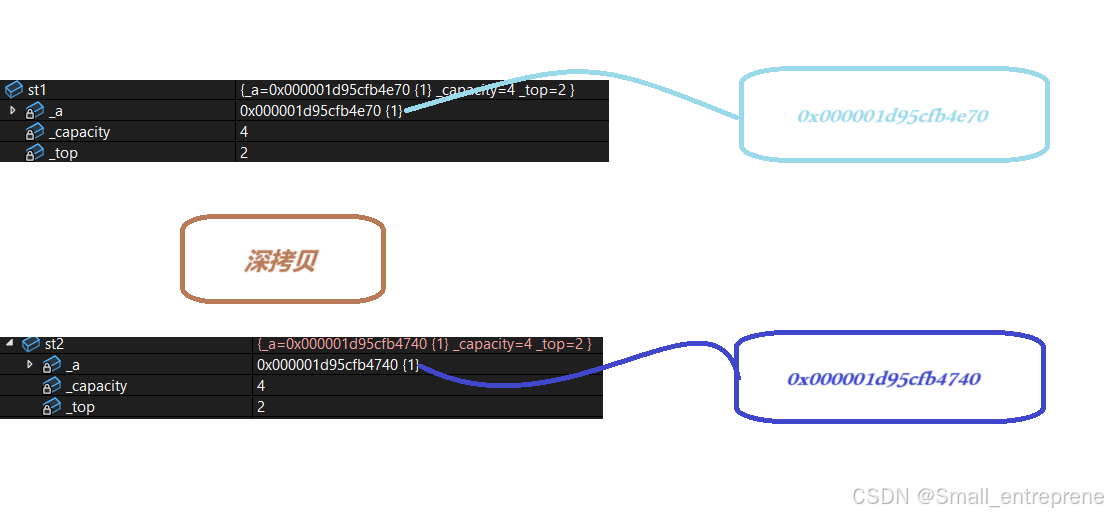
在public下,自己写一个拷贝构造:
- Stack(const Stack& st)
- {
- // 需要对_a指向资源创建同样⼤的资源再拷⻉值
- _a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);
- if (nullptr == _a)
- {
- perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");
- return;
- }
- memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);
- _top = st._top;
- _capacity = st._capacity;
- }
引用的好处:(体现)
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- typedef int STDataType;
- class Stack
- {
- public:
- Stack(int n = 4)
- {
- _a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);
- if (nullptr == _a)
- {
- perror("malloc申请空间失败");
- return;
- }
- _capacity = n;
- _top = 0;
- }
- Stack(const Stack& st)
- {
- // 需要对_a指向资源创建同样⼤的资源再拷⻉值
- _a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);
- if (nullptr == _a)
- {
- perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");
- return;
- }
- memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);
- _top = st._top;
- _capacity = st._capacity;
- }
- void Push(STDataType x)
- {
- if (_top == _capacity)
- {
- int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *
- sizeof(STDataType));
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc fail");
- return;
- }
- _a = tmp;
- _capacity = newcapacity;
- }
- _a[_top++] = x;
- }
- ~Stack()
- {
- cout << "~Stack()" << endl;
- free(_a);
- _a = nullptr;
- _top = _capacity = 0;
- }
- private:
- STDataType* _a;
- size_t _capacity;
- size_t _top;
- };
- void Func(Stack st)
- {
- }
- int main()
- {
- Stack st1;
- st1.Push(1);
- st1.Push(2);
- Func(st1);//这样是不行的,这时候st是st1的深拷贝,st的改变不会影响st1,另一个层度警示我们:自定义类型用传值传参不好,尽可能用引用,不改变时用const引用
- // Stack不显⽰实现拷⻉构造,⽤⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造完成浅拷⻉
- // 会导致st1和st2⾥⾯的_a指针指向同⼀块资源,析构时会析构两次,程序崩溃
- //Stack st2(st1);
- return 0;
- }
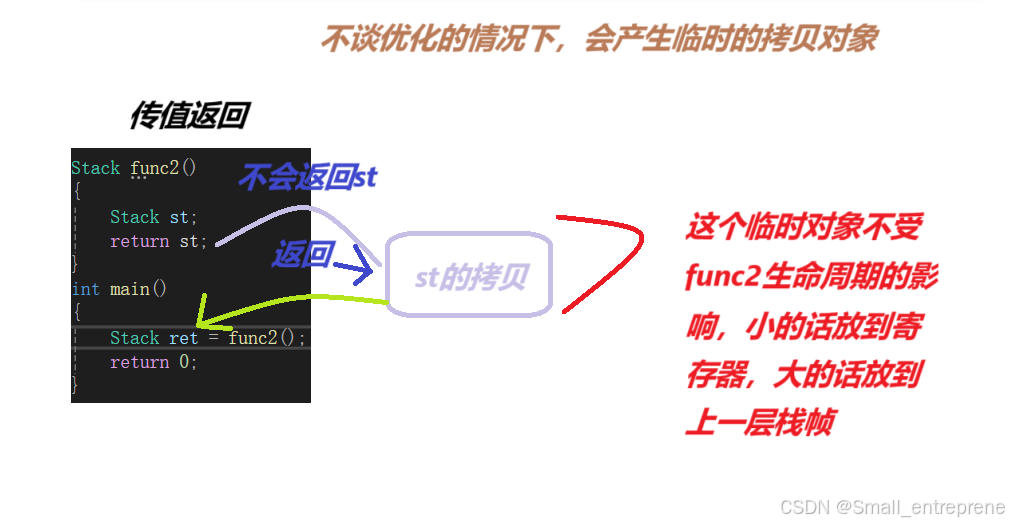 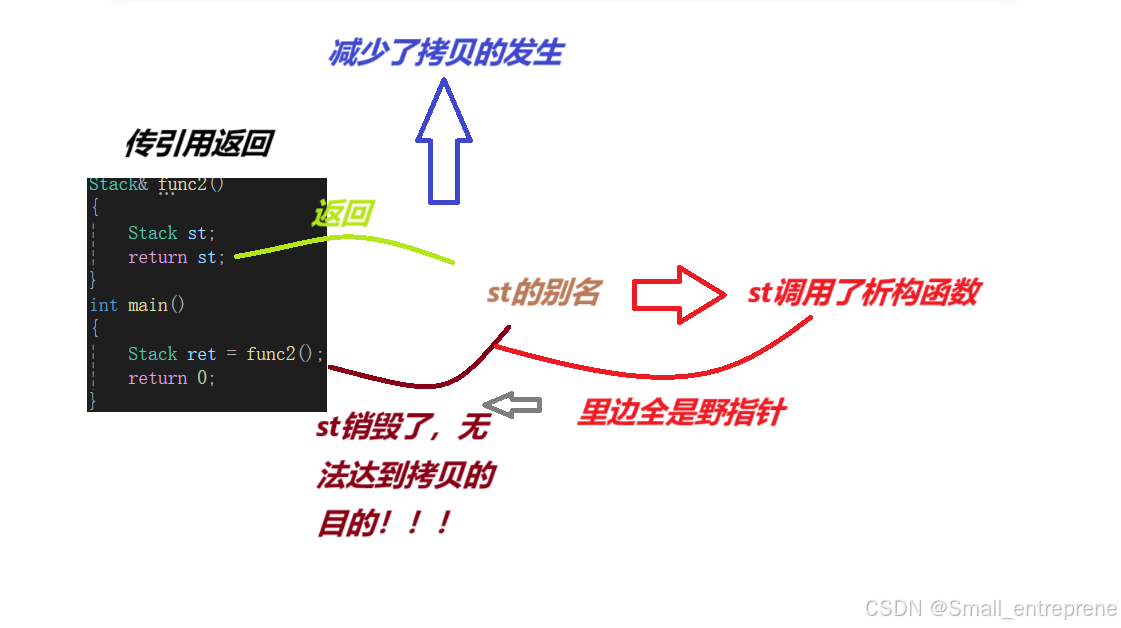 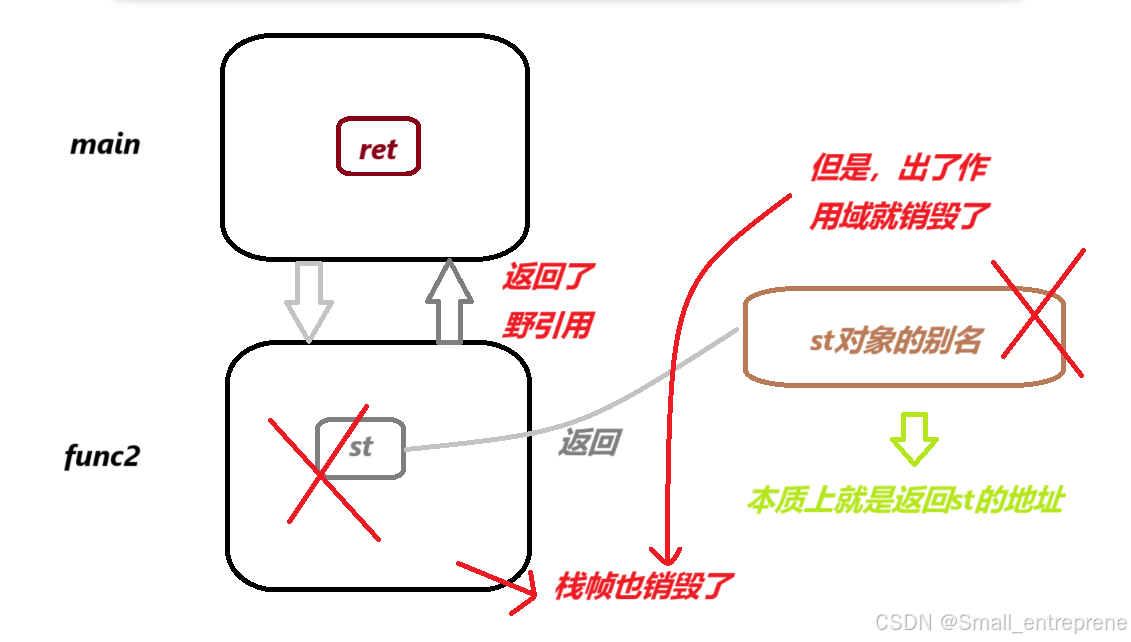
- Stack& func2()
- {
- static Stack st;//这时候是静态对象,全局对象了
- return st;
- }
- int main()
- {
- Stack ret = func2();
- return 0;
- }
- Stack func2(Stack& st)
- {
- st.Push(1);
- st.Push(1);
- st.Push(1);
- return st;
- }
- int main()
- {
- Stack st1;
- func2(st1);
- return 0;
- }
- cout << "Stack(const Stack& st)" << endl;//检验是否调用拷贝构造
1.运算符重载
• 当运算符被⽤于类类型的对象时,C++语⾔允许我们通过运算符重载的情势指定新的寄义。C++规定类类型对象使⽤运算符时,必须转换成调⽤对应运算符重载,若没有对应的运算符重载,则会编译报错;(运算符重载转化成一个函数) • 运算符重载是具有特殊名字的函数,他的名字是由operator(关键字)和后⾯要界说的运算符共同构成。和其他函数⼀样,它也具有其返回类型和参数列表以及函数体;(格式:operator+运算符 构成函数名) • 重载运算符函数的参数个数和该运算符作⽤的运算对象数量⼀样多,⼀元运算符有⼀个参数,⼆元运算符有两个参数,⼆元运算符的左侧运算对象传给第⼀个参数,右侧运算对象传给第⼆个参数;(++/- -/*(解引用)/.....就是一元) • 如果⼀个重载运算符函数是成员函数,则它的第⼀个运算对象默认传给隐式的this指针,因此运算符重载作为成员函数时,参数⽐运算对象少⼀个; • 运算符重载以后,其优先级和联合性与对应的内置类型运算符保持⼀致; - #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Date
- {
- public:
- Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
- {
- _year = year;
- _month = month;
- _day = day;
- }
- void Print()
- {
- cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
- }
- //Get函数
- int Get_year()
- {
- return _year;
- }
- int Get_month()
- {
- return _month;
- }
- int Get_day()
- {
- return _day;
- }
- //因为存在this指针,所以应当少一个
- bool operator==(Date d2)
- {
- return _year == d2._year
- && _month == d2._month
- && _day == d2._day;
- }
- private:
- int _year;
- int _month;
- int _day;
- //自定义类型怎么去比较?他的行为应该是我们自己去定义的,而不是系统去定义的
- };
- //比较大小的返回值是一个bool值
- bool operator<(Date d1, Date d2)
- {
- }
- //重载成全局的,方式是最正的:二元的:左操作数传给第一个参数,右操作数传给第二个参数
- //bool operator==(Date d1, Date d2)
- //{
- // return d1._year == d2._year
- // && d1._month == d2._month
- // && d1._day == d2._day;
- // //没有访问权限,1:可以直接将private的内容包含于public
- // //·······2:提供Get函数
- // //·······3:友元
- // //·······4:放在类里面成为成员函数
- //}
- int main()
- {
- Date x1(2024, 7, 16);
- Date x2(2024, 7, 16);
- 到底是x1对应d1,还是d2
- 可以显现调用(跟一个普通函数一样):
- //operator==(x1, x2);
- 还可以:
- //x1 == x2;
- //全局的和成员的都有,会优先调用成员的
- //改后:
- x1.operator==(x2);
- x1 == x2;
- return 0;
- }
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class A
- {
- public:
- void func()
- {
- cout << "A::func()" << endl;
- }
- };
- //用回调的方式去调用成员函数的指针
- //普通函数指针;void(*)();
- typedef void(A::* PF)(); //成员函数指针类型
- int main()
- {
- //void(A:: * PF)() = nullptr;
- PF pf = nullptr;
- //实现回调
- // C++规定成员函数要加&才能取到函数指针
- pf = &A::func;
- //普通的,全局的函数是可以回调的
- //(*pf)();//成员函数回调不了,因为有隐含的this指针
-
- //要调用函数指针,要传隐含的this指针这个实参
- A aa;
- //(*pf)(&aa);//这样也不行,因为this指针在形参和实参的位置不能显示
- //C++规定:回调成员函数的指针要这么回调:
- (aa.*pf)();//aa就悄悄传给this
- }
- d1 + 100;//100天后日期是多少
- d1 - 100;//100天前日期是多少
- d1 - d2;//间隔天数
- //d1+100
- Date operator+(int day);
- //d1-100
- Date operator-(int day);
- //d1-d2
- int operator-(const Date& d);
• 重载++运算符时,有前置++和后置++,运算符重载函数名都是operator++,⽆法很好的区分, C++规定,后置++重载时,增加⼀个int形参,跟前置++构成函数重载,⽅便区分; • 重载<<和>>时,需要重载为全局函数,由于重载为成员函数,this指针默认抢占了第⼀个形参位 置,第⼀个形参位置是左侧运算对象,调⽤时就变成了 对象<<cout,不符合使⽤习惯和可读性。 重载为全局函数把ostream/istream放到第⼀个形参位置就可以了,第⼆个形参位置当类类型对 象; 2.赋值运算符重载
赋值运算符重载是⼀个默认成员函数,⽤于完成两个已经存在的对象直接的拷⻉赋值,这⾥要注意跟拷⻉构造区分,拷⻉构造⽤于⼀个对象拷⻉初始化给另⼀个要创建的对象 - int main()
- {
- Date d1(2024, 7, 5);
- Date d2(2024, 7, 6);
-
- //赋值重载拷贝
- d1 = d2;
- //拷贝构造
- Date d3(d2);
- Date d4 = d2;
- return 0;
- }
1. 赋值运算符重载是⼀个运算符重载,规定必须重载为成员函数(不可以是全局)。赋值运算重载的参数建议写成 const 当前类类型引⽤,否则会传值传参会有拷⻉; - void operator=(const Date& d)
- {
- //尽管用传值传参,不会产生所谓的无穷递归,现在是赋值重载,传值传参,把d2传给d,调用拷贝构造,调用完回来了,接着调用赋值
- //operator赋值//但是建议用引用
- _year = d._year;
- _month = d._month;
- _day = d._day;
- }
- bool operator==(const Date& d)
- {
- //拷贝构造赋值重载拷贝去传值传参形成新的拷贝构造。。。。。无穷递归
- //operator等于
- }
2. 有返回值 ,且建议写成当前类类型引⽤,引⽤返回可以提⾼效率, 有返回值⽬的是为了⽀持连赋 值场景 ; - Date operator=(const Date& d)
- {
- _year = d._year;
- _month = d._month;
- _day = d._day;
- //d3=d1
- //this是d3的地址
- return *this;//类里面可以显示写
- }
- Date& operator=(const Date& d)
- {
- _year = d._year;
- _month = d._month;
- _day = d._day;
- return *this;
- }
3.日期类实现
补充:两个日期间隔多少天(有算正负数)-----算法:图解:
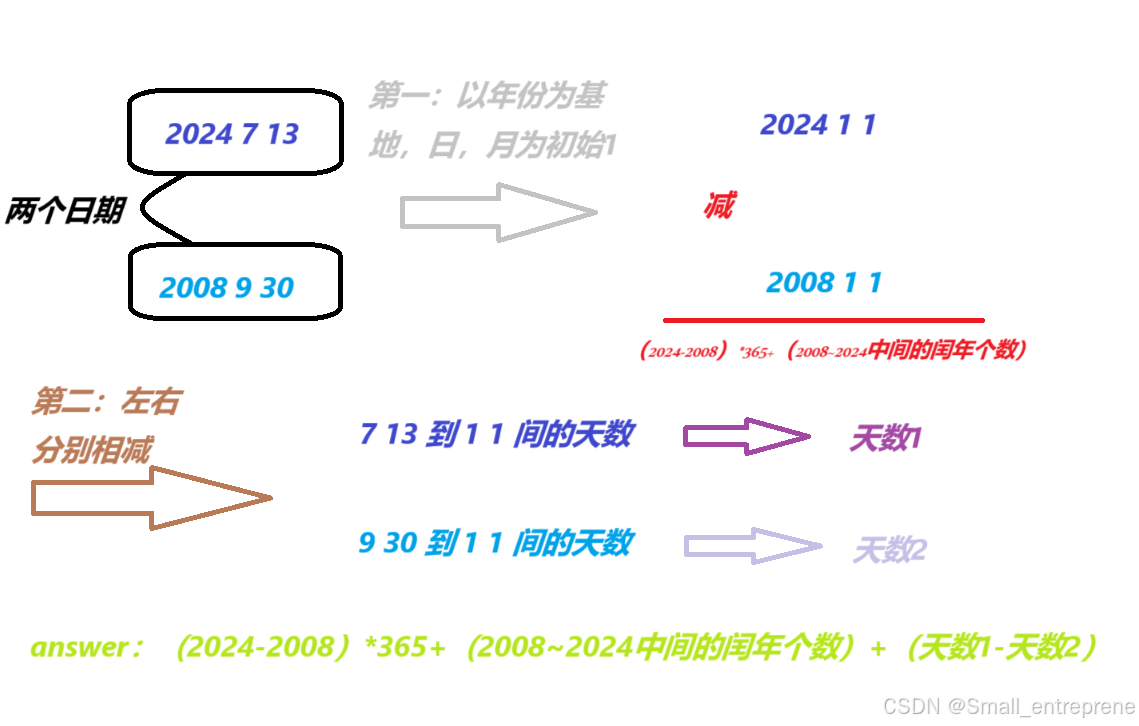
另外:还可以尽可能复用逻辑(代码中会演示到):取小日期(比较巨细),让小的日期不断++,真到与大日期相称:(不过相比于上图方法,会相对慢,但cpu太快了,无所谓)
代码:
头文件:Date.h
- #pragma once
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- #include<assert.h>
- class Date
- {
-
- //我和小笨蛋不认识,所以不可以去他家玩,但我很想去,因为他爸爸会数分,就给小笨蛋吹彩虹屁,就和他成为朋友了
- //友元声明:friend+函数声明
- friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
- friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
- public:
- bool CheckDate();
- Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);
- void Print()const;
- //频繁调用的小函数
- //没有做声明和定义分离, 因为定义在类里面的成员函数默认是内联inline
- int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
- {
- //防止month在减的时候是从一月减到零月:
- assert(month > 0 && month < 13);
- //因为要频繁调用,所以放到静态区去
- static int monthDayArray[13] = { -1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
- if ((month == 2) && (year % 100 != 0 && year % 4 == 0) || (year % 400 == 0))
- {
- return 29;
- }
- return monthDayArray[month];
- }
- bool operator<(const Date& d)const;
- bool operator<=(const Date& d)const;
- bool operator>(const Date& d)const;
- bool operator>=(const Date& d)const;
- bool operator==(const Date& d)const;
- bool operator!=(const Date& d)const;
- Date operator+(int day)const;
- Date& operator+=(int day);
- Date operator-(int day)const;
- Date& operator-=(int day);
- d1++
- //Date operator++();
- ++d1
- //Date operator++();
- //这么区分这两个(d1++,++d1):重载++运算符时,有前置++和后置++,运算符重载函数名都是operator++,⽆法很好的区分。
- //C++规定,后置++重载时,增加⼀个int形参,跟前置++构成函数重载,⽅便区分。
- //d1++:后置++
- Date operator++(int);
- //++d1:前置++
- Date& operator++();
- Date operator--(int);
- Date& operator--();
- //d1-d2
- int operator-(const Date& d);
- //printf与scanf他们直接适应的是内置类型
- //流插入之所以可以自定识别类型,是因为本质是函数重载
- //void operator<<(ostream& out);//写成成员函数是为了访问私有,但是这个实现形式倒反天罡
- private:
- int _year;
- int _month;
- int _day;
- };
- //全局
- //流插入
- ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
- //用友元声明:让类外面的函数访问类里面的元素
- //可是连续输出又不行:EG:cout<<d1<<d2
- //流插入是从左到右(赋值相反),所以应该返回out
- //流提取
- istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);//提取的值要放到Date对象中,所以不加const
- #include"Date.h"
- bool Date::CheckDate()
- {
- if (_month < 1 || _month > 12
- || _day < 1 || _day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
- {
- return false;
- }
- else
- {
- return true;
- }
- }
- Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- _year = year;
- _month = month;
- _day = day;
- if (!CheckDate())
- {
- cout << "非法日期" << endl;
- Print();
- }
- }
- void Date::Print() const
- {
- cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
- }
- //这是+=:会改变_day
- Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
- {
- //有坑:当day为负数时:
- // 解决:
- if (day < 0)
- {
- return *this -= (-day);
- }
- //与加法进数一样,天满了往月上进位,月满了往年进位
- _day += day;
- while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
- {
- _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
- _month++;
- if (_month == 13)
- {
- _year++;
- _month = 1;
- }
- }
- return*this;
- }
- //d1+100:不会改变d1
- Date Date::operator+(int day)const
- {
- //拷贝构造的场景
- Date tmp = *this;
- //+=就会往tmp上走
- /*tmp._day += day;
- while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
- {
- tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
- tmp._month++;
- if (tmp._month == 13)
- {
- tmp._year++;
- tmp._month = 1;
- }
- }*/
- //复用:
- tmp += day;
- return tmp;//tmp为局部对象,出了作用域销毁,不能用引用返回,即使会多进行一次拷贝
- }
- Date& Date:: operator-=(int day)
- {
- if (day < 0)
- {
- return *this += (-day);
- }
- _day -= day;
- while (_day <= 0)
- {
- _month--;
- if (_month == 0)
- {
- _month = 12;
- }
- _day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
- }
- return *this;
- }
- Date Date:: operator-(int day)const
- {
- Date tmp = *this;
- /*tmp._day -= day;
- while (tmp._day <= 0)
- {
- tmp._month--;
- if (tmp._month == 0)
- {
- tmp._month = 12;
- }
- tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
- }*/
- tmp -= day;
- return tmp;
- }
- d1-=100
- 用-实现-=:d1改变
- //Date& Date:: operator-=(int day)
- //{
- // /*Date tmp = *this - day;
- // *this = tmp;*/
- // *this = *this - day;
- // return *this;
- //}
- //其实-复用-=更好:因为-的效率本身是更低的
- //:
- //Date tmp = *this;是一次拷贝,return *this 传值返回也是一次拷贝
- //-复用-=或-=复用-,在“-”中,都要进行两次构造,所以,真正的区别在于-=
- //如果-=是自己实现,全程没有拷贝;
- //但是-=去复用-,就会加上-带来的两次拷贝和多加的赋值拷贝,很亏
- //至少实现<+=或>+=
- bool Date:: operator<(const Date& d)const
- {
- if (_year < d._year)
- {
- return true;
- }
- else if (_year == d._year)
- {
- if (_month < d._month)
- {
- return true;
- }
- else if (_month == d._month)
- {
- return _day < d._day;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- //d1<=d2
- bool Date:: operator<=(const Date& d)const
- {
- return *this < d || *this == d;
- }
- bool Date:: operator>(const Date& d)const
- {
- /*if (_year > d._year)
- {
- return true;
- }
- else if (_year == d._year)
- {
- if (_month > d._month)
- {
- return true;
- }
- else if (_month == d._month)
- {
- return _day > d._day;
- }
- }
- return false;*/
- return !(*this <= d);
- }
- bool Date:: operator>=(const Date& d)const
- {
- return !(*this < d);
- }
- bool Date:: operator==(const Date& d)const
- {
- return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;
- }
- bool Date:: operator!=(const Date& d)const
- {
- return !(*this == d);
- }
- //d1++
- //d1.operator(0);
- Date Date::operator++(int)
- {
- Date tmp = *this;
- *this += 1;
- return tmp;
- }
- //++d1
- //d1.operator();
- Date& Date::operator++()
- {
- *this += 1;
- return *this;
- }
- //所以:能用前置就用前置:引用返回:少拷贝
- Date Date::operator--(int)
- {
- Date tmp = *this;
- *this -= 1;
- return tmp;
- }
- Date& Date::operator--()
- {
- *this -= 1;
- return *this;
- }
- //天数的实现
- int Date:: operator-(const Date& d)
- {
- int flag = 1;
- int n = 0;
- //假设法
- Date max = *this;
- Date min = d;
- if (*this < d)
- {
- max = d;
- min = *this;
- flag = -1;
- }
- while (min != max)
- {
- ++min;
- ++n;
- }
- return n * flag;
- }
- //倒反天罡
- //void Date::operator<<(ostream& out)
- //{
- // //out就是cout
- // //对于二元函数,默认左操作数对应第一个参数
- // out << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;
- // //要这么配得上:d1<<out//d1.operator<<(cout)
- //}
- //因为流对象中含有指向IO缓冲区的指针,假如流对象可以复制,那么将会有两个指针同时操作缓冲区,如何释放、如何修改都会有冲突同步问题,因此流对象无法复制。
- ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
- {
- out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
- return out;
- }
- istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
- {
- while (1)
- {
- cout << "请依次输入年月日:>";
- in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
- //在进行流提取是,cout的buffer刷新了,be flushed了
- if (!d.CheckDate())
- {
- cout << "输入日期非法";
- d.Print();
- cout << "请重新输入:" << endl;
- }
- else
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- return in;
- }
1.const成员函数
• 将const修饰的成员函数称之为const成员函数,const修饰成员函数放到成员函数参数列表的后⾯; • const实际修饰该成员函数隐含的this指针,表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进⾏修改。 const 修饰Date类的Print成员函数,Print隐含的this指针由 Date* const this 变为 const Date* const this - void Date::Print()
- {
- cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
- }
- const Date d1(2024, 7, 19);
- d1.Print();
- //权限放大
- void Date::Print() const
- {
- cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
- }
- const Date d1(2024, 7, 19);
- d1.Print();
- Date d2(2024, 7, 20);
- d2.Print();
- //权限可以缩小
2.取地点运算符重载
取地点运算符重载分为普通取地点运算符重载和const取地点运算符重载,⼀般这两个函数编译器⾃动 ⽣成的就可以够我们⽤了,不需要去显⽰实现。除⾮⼀些很特殊的场景,⽐如我们不想让别⼈取到当前类对象的地点,就可以⾃⼰实现⼀份,胡乱返回⼀个地点 - #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Date
- {
- public:
- //两个都写,优先取合适的
- Date* operator&()
- {
- return this;
- // return nullptr;
- //使坏:
- //return (Date*)0x2673FF40;
- }
- const Date* operator&()const
- {
- return this;
- // return nullptr;
- //return (Date*)0x2673FF40;
- }
- private:
- int _year; // 年
- int _month; // ⽉
- int _day; // ⽇
- };
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作!更多信息从访问主页:qidao123.com:ToB企服之家,中国第一个企服评测及商务社交产业平台。 |